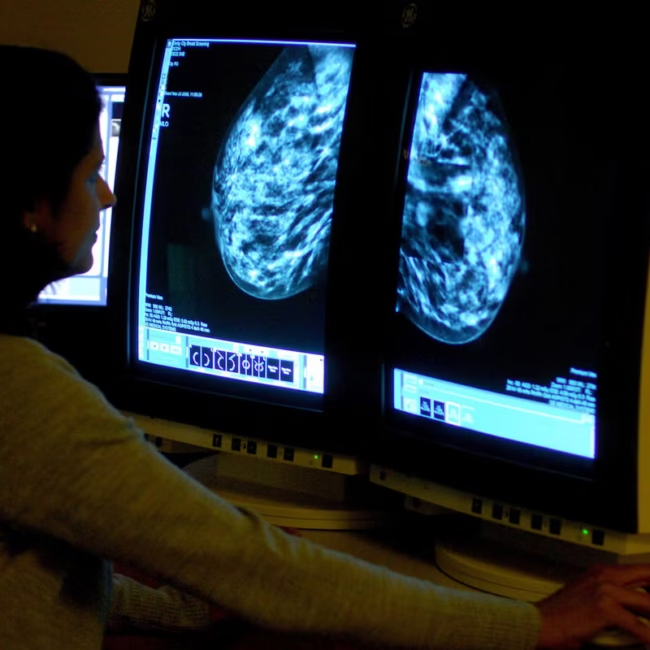
A recent study by the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center has identified microRNA-205 (miR-205) as a key regulator in breast cancer treatment resistance. Researchers discovered that miR-205 inversely correlates with MED1 protein levels, which are elevated in 40% to 60% of breast cancers and contribute to antiestrogen therapy resistance. By targeting miR-205, it may be possible to modulate MED1 expression, potentially overcoming treatment resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers.
The study also highlights the broader significance of noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs, which constitute approximately 90% of the human genome and play crucial roles in gene regulation. The discovery of microRNAs’ functions was recognized with the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024. This research underscores the potential of targeting noncoding RNAs like miR-205 to develop novel therapeutic strategies for treatment-resistant breast cancers. Click for More Details