Cancer Biology & Mechanisms
-
Facebook
-
Twitter
-
Linkedin
This category explores the fundamental science behind how cancer begins, develops, and spreads. Articles in this section delve into the genetic mutations, molecular pathways, and cellular processes that drive cancer progression. Topics may include tumor microenvironments, genomic instability, cell signaling, DNA repair mechanisms, and emerging insights into metastasis and inflammation in cancer. By understanding these biological foundations, researchers can identify new targets for future diagnostics and therapies.

TROPION-Lung12 phase 3 trial initiated evaluating Datroway as part of adjuvant regimen for patients with early-stage NSCLC at high risk of relapse
he first patient has been dosed in the TROPION-Lung12 phase 3 trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of adjuvant Datroway (datopotamab deruxtecan) plus rilvegostomig or rilvegostomig monotherapy versus standard of care in patients with stage 1 adenocarcinoma non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after complete surgical resection who are ctDNA-positive or have other high risk pathological features.
Targeting MYCN and MDM2 offers new hope for cancer therapy
Over the past two decades, the idea of targeting transcription factors to combat malignancies has turned into a clinical reality.

Biomarker predicts KRASG12C inhibitor success in lung cancer treatment
A new study from Moffitt Cancer Center could help doctors predict how well patients with a specific type of lung cancer will respond to new therapies. The research, published in Clinical Cancer Research, found that measuring the interaction between two proteins, RAS and RAF, could provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of treatments for patients with KRASG12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, a type of lung cancer known for being particularly difficult to treat.
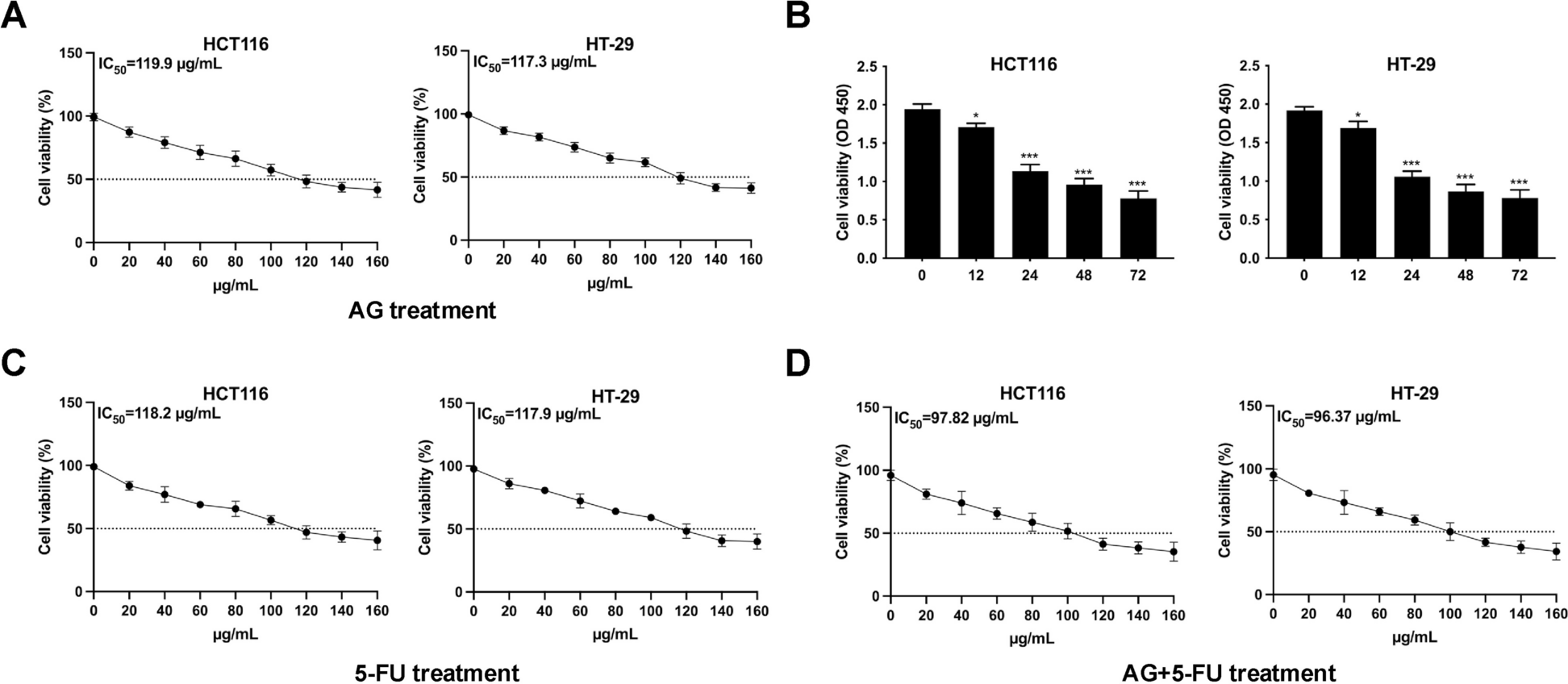
Amarogentin suppresses cell proliferation and EMT process through inducing ferroptosis in colorectal cancer – BMC Gastroenterology
Background Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one common tumor with the high death rate, and badly affects the normal lives of CRC patients. Amarogentin (AG) has been found to exhibit regulatory roles and join into the progression of multiple diseases. However, the regulatory impacts and associated molecular mechanisms of AG in CRC progression keep unclear. Methods and results In this study, it was demonstrated that AG weakened CRC cell viability in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. In addition, AG accelerated cell apoptosis by triggering ferroptosis. The cell invasion and EMT process were restrained after AG treatment, but these impacts were reversed after Fer-1 addition. Moreover, it was uncovered that AG retarded Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 activation. Additionally, AG modulated PTC cell viability and stimulated ferroptosis. At last, it was illustrated that AG suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Conclusion In conclusion, it was disclosed that AG suppressed cell proliferation and EMT process through inducing ferroptosis in CRC, and retarded Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 activation. This discovery suggested that AG may be one effective drug for ameliorating CRC progression.
New research shines light on position-specific hallmarks of cancer
A team led by the Cancer Immunogenomics group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute, the Computational Biology group at the Barcelona Supercomputing Center and the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute shows, for the first time, that within a tumor, the expression of the different hallmarks of cancer is not cell-specific, but rather position-specific.

Researchers use “hallmarks of cancer” to understand tumour growth
A team led by the Cancer Immunogenomics group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute, the Computational Biology group at the Barcelona Supercomputing Center and the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute shows, for the first time, that within a tumour, the expression of the different hallmarks of cancer is not cell-specific, but rather position-specific.
Research Spotlight: Advances in Pancreatic Cancer Research and Key Insights from ASCO GI 2025
PanCAN Chief Scientific & Medical Officer Dr. Anna Berkenblit outlines the latest advances in pancreatic cancer and offers key insights from ASCO GI 2025.

Medicinal plant has great potential to fight colorectal cancer
Artemisia herba-alba shows promise in combating colorectal cancer, offering new hope through its powerful medicinal properties.
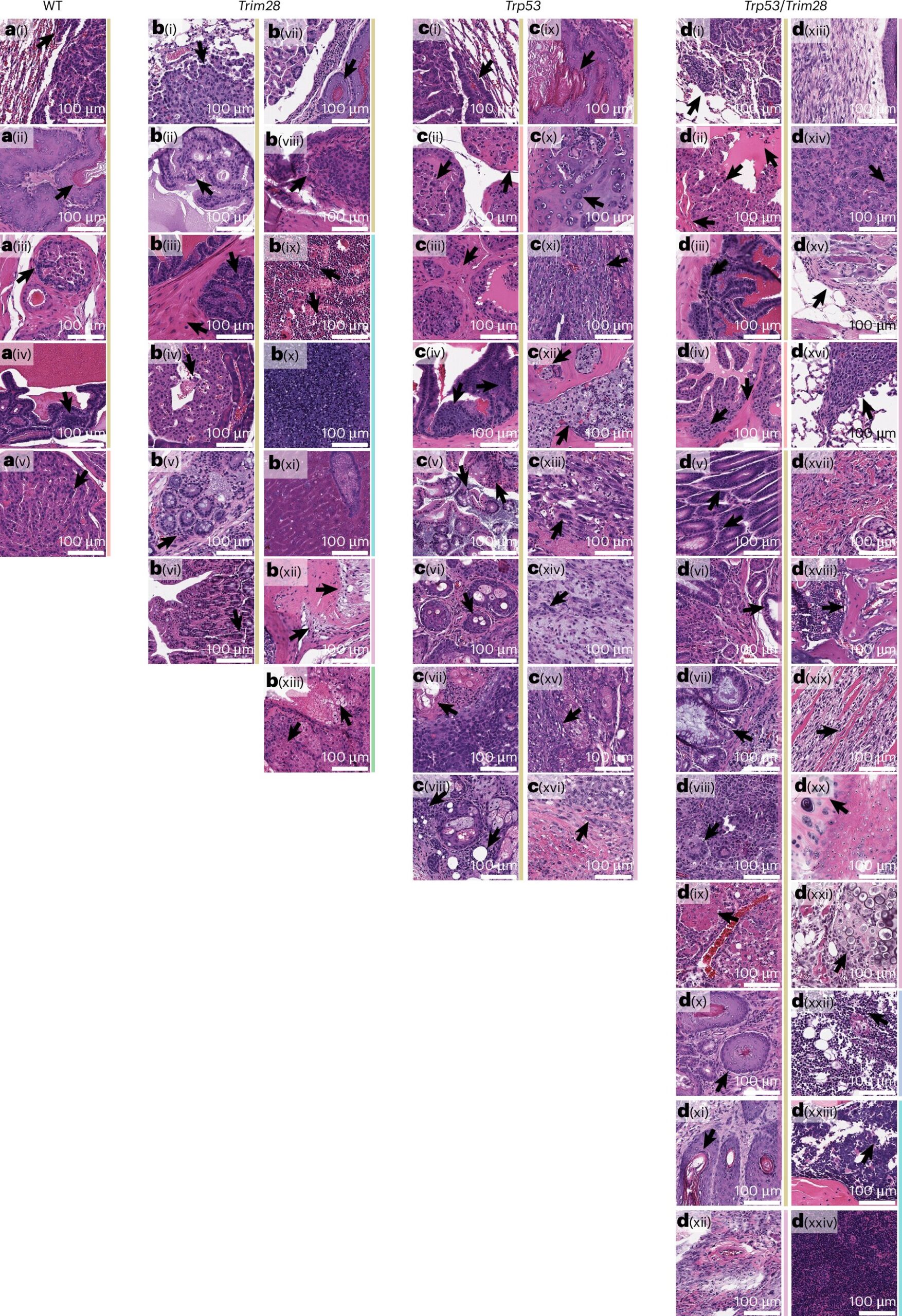
Epigenetic states during development establish cancer risk before birth
A person’s lifetime risk for cancer may begin before they are even born, reports a paradigm-shifting study by Van Andel Institute scientists.

Aromatic plant can fight colorectal cancer, say scientists
Scientists from the University of Sharjah have found that a naturally growing aromatic plant contains ingredients with the ability to treat colorectal cancer.

Research shows deep cause of cancer development
Research shows deep cause of cancer development

Revolutionary’ move in curing cancer on the horizon
A biotech company’s CEO discusses upcoming revolutionary approaches in cancer treatment, highlighting the role of new technologies.
FDA Approves Amgen Treatment For Pretreated Colorectal Cancer With Certain Mutation – Amgen (NASDAQ:AMGN) – Benzinga
Amgen’s Lumakras treatment, combined with Vectibix, is FDA-approved for KRAS G12C-mutated colorectal cancer.

The #1 Cancer-Fighting Food To Eat Because It ‘Slows Tumor Growth’ And Blocks Its Ability To Spread, Health Expert Reveals | SHEfinds
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body.

BeiGene wins US nod for Tevimbra label expansion (BGNE:NASDAQ) | Seeking Alpha
BeiGene (BGNE) has received U.S. FDA approval for its cancer drug Tevimbra in combination with chemotherapy for certain gastric carcinoma. Read more here.

Glass of milk a day cuts bowel cancer risk – study – BBC News
Dark leafy greens, bread and non-dairy milks containing calcium were also found to offer protection.

Chimerix files FDA application for brain cancer treatment – Triangle Business Journal
The Durham company is seeking a fast track to regulatory approval for its brain cancer treatment.

FDA sets priority review date for Verastem Oncology’s new ovarian cancer drug – Boston Business Journal
The FDA is aiming to make a decision about the treatment before the end of June.

AI increases chances to detect breast cancer, study finds
Researchers have indicated the use of AI in breast cancer screening increases the chances of detecting the disease. There have been claims that AI could Researchers have indicated the use of AI in breast cancer screening increases
FDA Approves Datroway for Pretreated Advanced Breast Cancer
In trial, datopotamab deruxtecan increased progression-free survival by 2 months
Protein CD74 can predict immunotherapy response in bowel cancer, independent of subtype
Bowel cancer is the fourth most common cancer in the UK, and the second most common cause of cancer death. The disease falls into two types: one where proteins that repair errors in DNA are missing or deficient (the deficient subtype), and one where this machinery is intact (the proficient subtype).

Putting a lid on excess cholesterol to halt bladder cancer cell growth
Like all cancers, bladder cancer develops when abnormal cells start to multiply out of control. But what if we could put a lid on their growth?

Research shows big cause of pancreatic cancer and how to treat it
big cause of pancreatic cancer and how to treat it