Esophageal
-
Facebook
-
Twitter
-
Linkedin
Advancements in endoscopic screening methods and minimally invasive surgery have improved patient outcomes. Research into molecular targets is paving the way for personalized treatments.

China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) Approves VYLOYª (zolbetuximab) for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma
OKYO, Jan. 5, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Astellas Pharma Inc. (TSE:4503, President and CEO: Naoki Okamura, “Astellas”) today announced that China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has approved VYLOYª (zolbetuximab), in combination with fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy, for the first-line treatment of patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma whose tumors are claudin (CLDN) 18.2 positive.
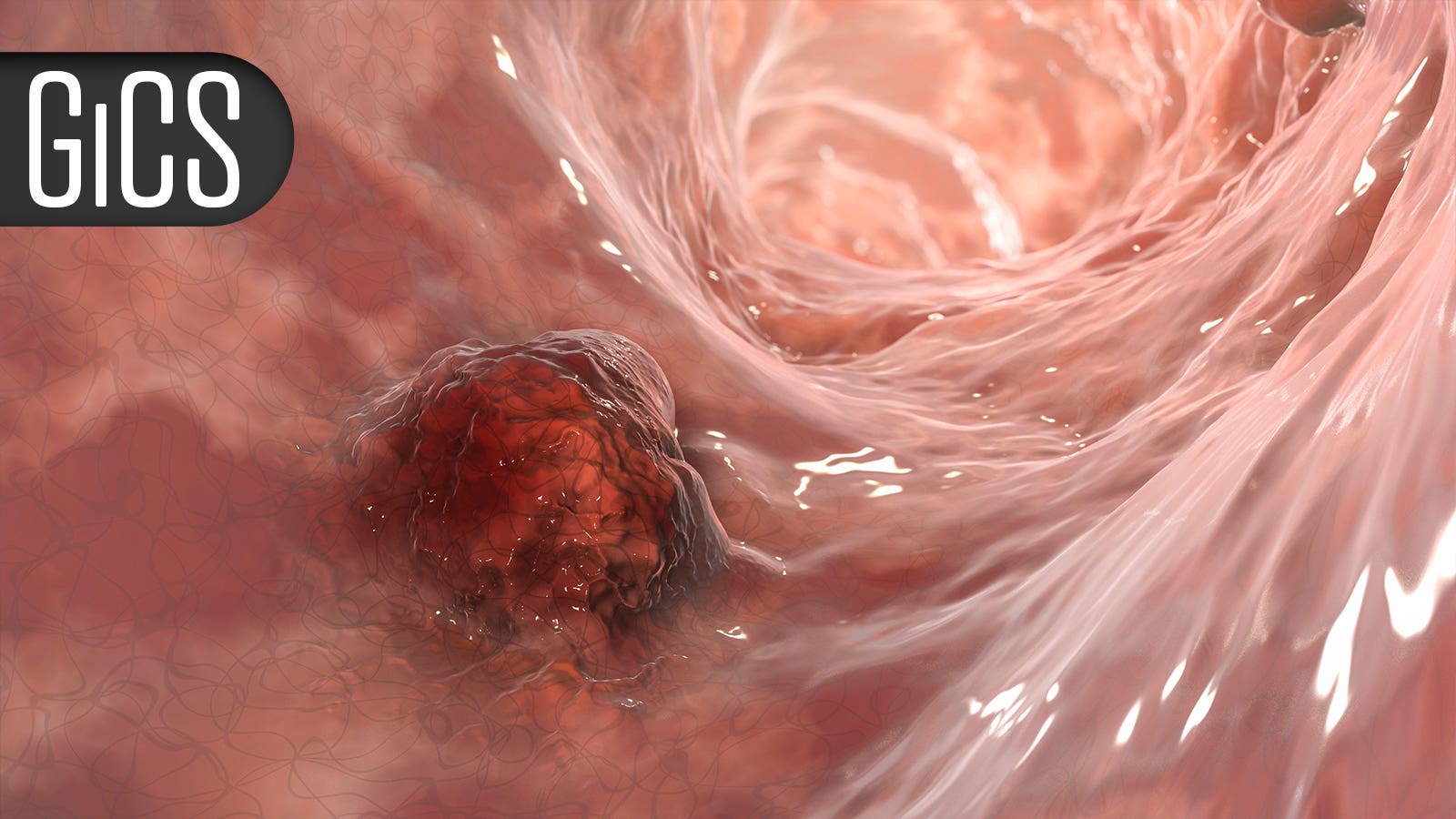
High Success Rate With Conversion Therapy for Unresectable Gastroesophageal Cancer
Three-fourths of patients had clear margins after surgery
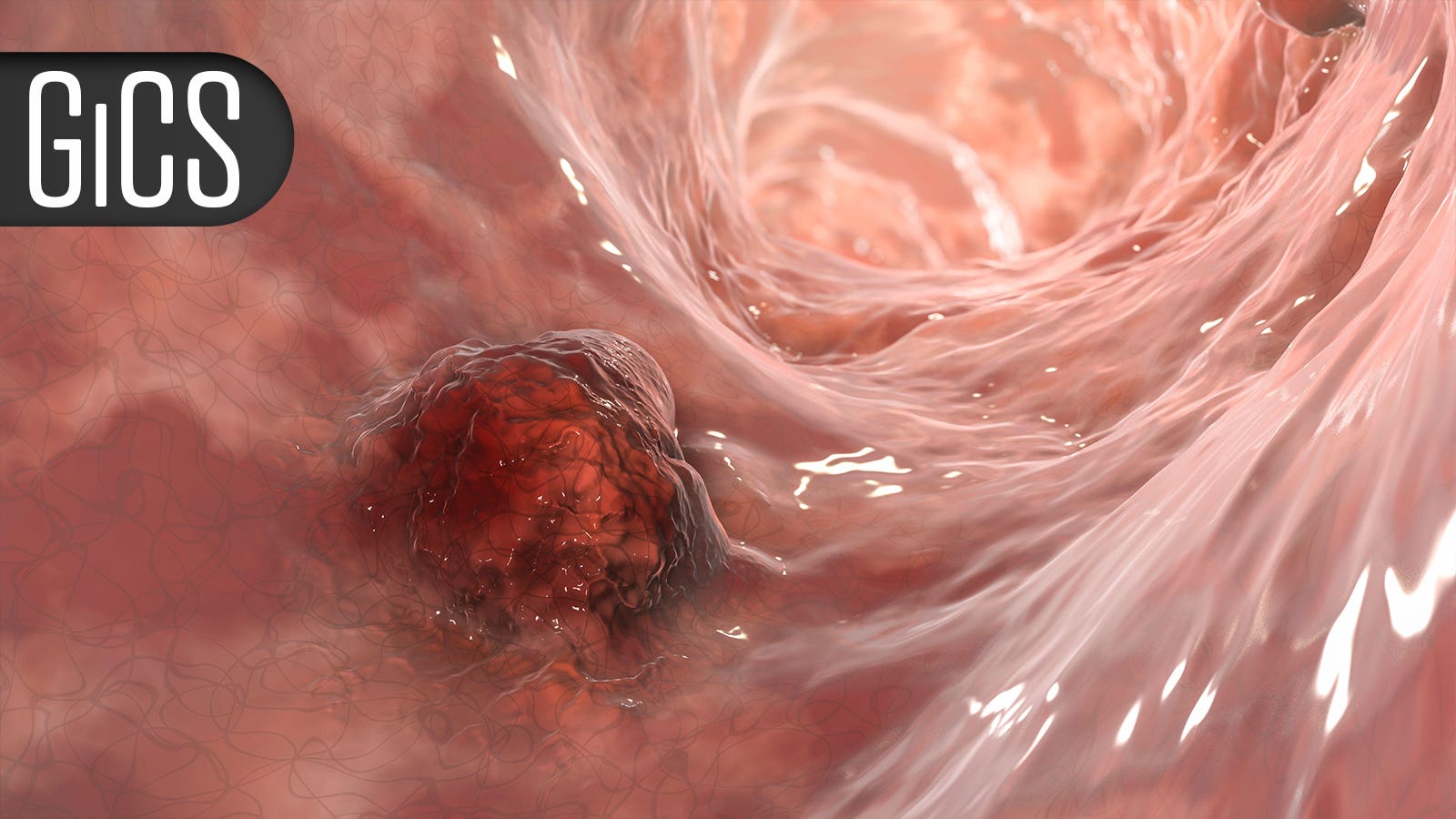
Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Plus Immunotherapy Boosts Responses in Esophageal Cancer
Phase III trial suggests regimen ‘has the potential to become the new standard of care’
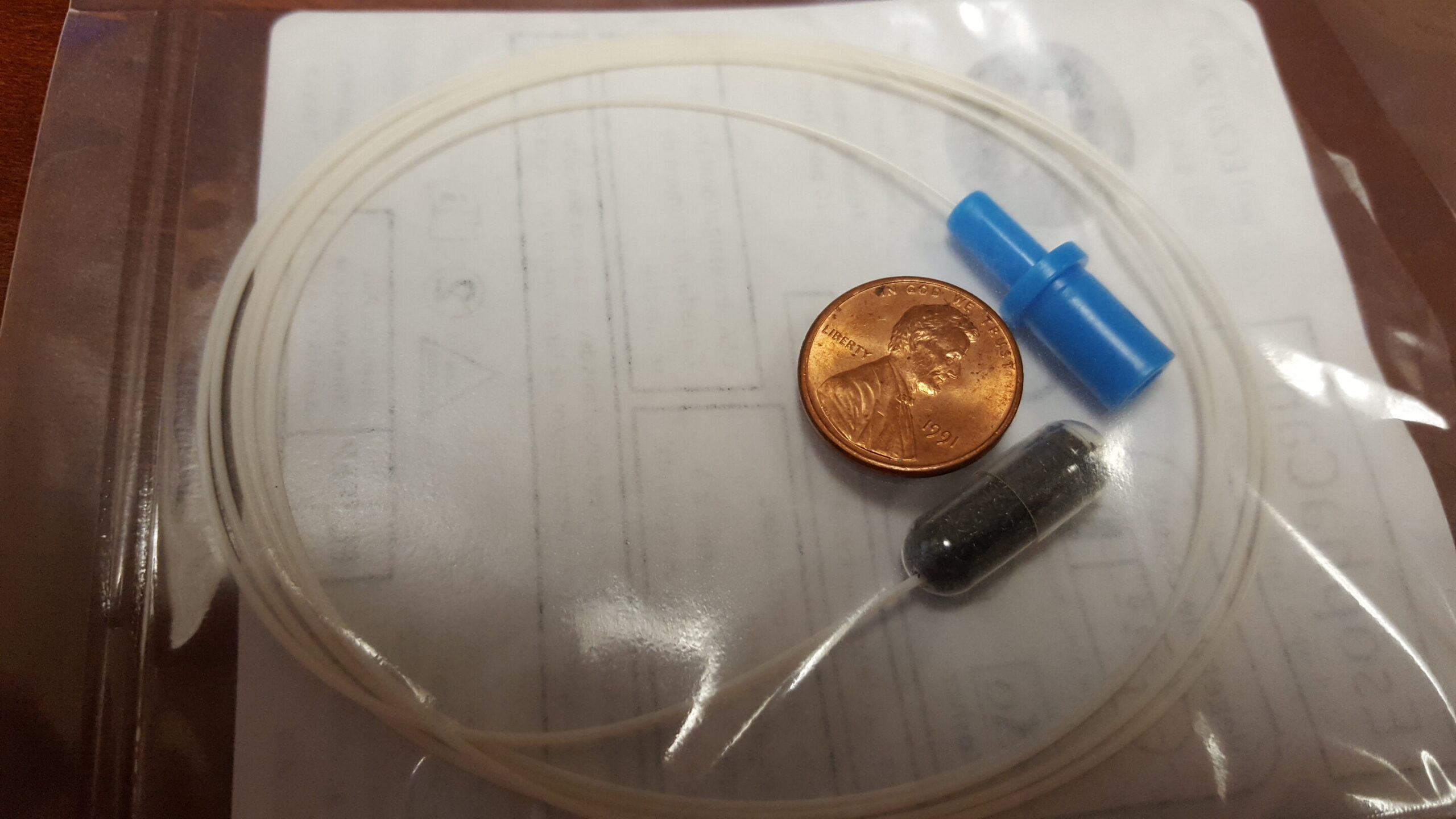
Biomarker algorithm for Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer developed
By studying biomarkers known to be involved in gastrointestinal cancers, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine have developed a biomarker algorithm that, when combined with a noninvasive method to collect esophageal cells for study, could give clinicians insight into which patients [SJMM1] have esophageal cancer or precancerous conditions such as Barrett’s esophagus (BE) or high-grade dysplasia. Typically, such determinations are made by endoscopy, an invasive procedure performed with patients under anesthesia.